14 Feb Sugar cane

Sugar cane is a noble plant. I tell you his story:
It belongs to the family of grasses (Poaceae), perennial plants, such as wheat, rice, maize or bamboo and others. At maturity, it can reach up to six meters in height and a diameter of 3 to 5 cm and contains a sap which is sucrose (sucrose, one of the most common dietary sugars in nature). There are other varieties of sugar cane such as: spontaneum, chinense, barberu used for the creation of hybrids because they are more resistant to climate and soil.
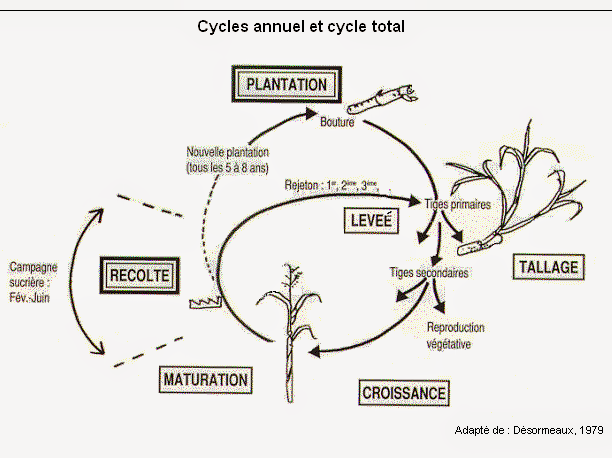
Sugarcane can reproduce without degenerating for about 6 years. There are two cycles of the cane:
- from plantation to plantation
Duration of 3 to 10 years depending on the country
- from cutting to cutting: duration 2 years maximum (ex: case of Hawaii)

SOURCE: THE SUGAR CANE FARMERS MANUAL, CTCS-Martinique, du Lamentin., 1994
The cycle from planting to first harvest includes the following steps:
- Planting
- lifting
- Tillering
- Growth (aboveground and belowground)
- Signage
- Technological maturity
- Harvest
Its origin comes from Oceania, New Guinea and other Pacific islands where it was cultivated. Extracted in India and China. Then introduced into Persia in the 6th century then propagated by the Arabs in the 7th century all around the Mediterranean (Cyprus, ridge, Spain). Imported into Europe where it will only be used by apothecaries Possessing medicinal properties, it is given a pharmaceutical name Saccharum officinarum (known as noble cane).
Due to the rise of social classes and a taste for luxury, Italian cities such as Venice and Genoa established trade with Eastern cities for sugar cane and white granulated sugar. found this sugar cane in the Balearic Islands, Portugal, Canary Islands. Christopher Columbus introduced it to the West Indies then to Central America, Santo Domingo, Cuba, Mexico, Louisiana.
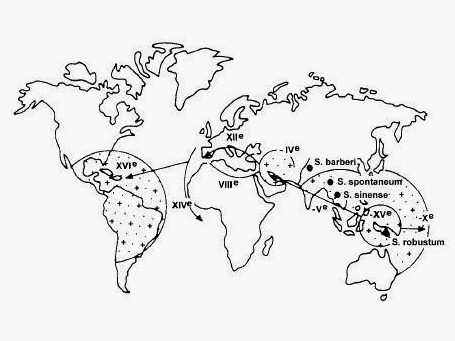
Diffusion of the noble cane, Saccharum officinarum, from New Guinea (graphic: after Fahrasmane-Ganou-Parfait, INRA, site: www.lameca.org)
Sugar cane is harvested between February and June in the West Indies, when the sugar concentration is optimal and at the level of the lower part of the stem.
It is here and at ground level that the sugar cane is cut. The upper part called the head or “white end” is eliminated. However, the sugar cane must be processed immediately and passed to the mill less than 36 hours after its cutting because the heat activates its fermentation and makes the extraction of the sugar difficult.

